
- #VPN REPLACEMENT FOR MAC SIERRA INSTALL#
- #VPN REPLACEMENT FOR MAC SIERRA SERIAL#
Once you’ve chosen your directory service configuration, if you require a third DNS server, click on Advanced DNS and then enter it, or any necessary search-domains. If the system hasn’t been authenticated to a directory server, do so using the Users & Groups” System Preference pane. The Directory Authentication screen allows you to choose which directory services to make available to PPTP or L2TP. If you configure Directory Authentication, you’ll get prompted that it might be buggy.
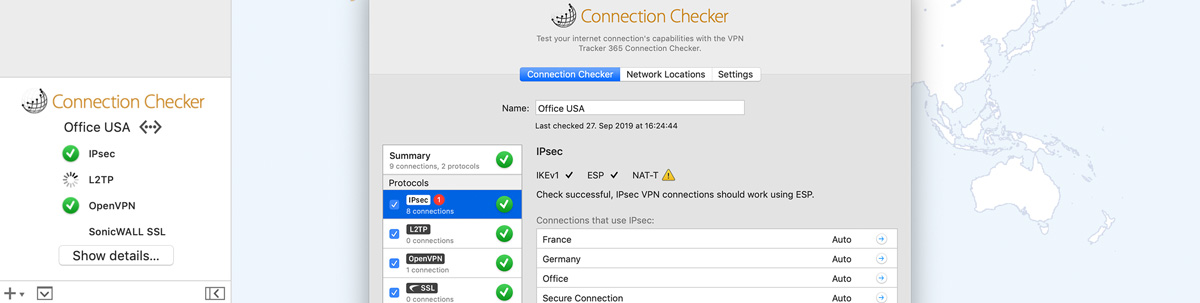 VPN Host Name: Used for the configuration profile so a client system can easily find the server w. When imported into a Mac or iOS device, that profile automatically configures the connection to the PPTP or L2TP service you’ve setup. Export Configuration Profile: Exports a configuration profile. Configure Static Routes: Allows you to specify the interface and netmask used to access a given IP. Advanced DNS: Allows you to configure DNS servers as well as Search Domains. Basic DNS: Allows you to configure a primary and second DNS server to send to clients via DHCP when they connect to the VPN interface. When configuring the range, take care not to enter a range of addresses in use by any other DHCP services on your network or you will end up with conflicts.
VPN Host Name: Used for the configuration profile so a client system can easily find the server w. When imported into a Mac or iOS device, that profile automatically configures the connection to the PPTP or L2TP service you’ve setup. Export Configuration Profile: Exports a configuration profile. Configure Static Routes: Allows you to specify the interface and netmask used to access a given IP. Advanced DNS: Allows you to configure DNS servers as well as Search Domains. Basic DNS: Allows you to configure a primary and second DNS server to send to clients via DHCP when they connect to the VPN interface. When configuring the range, take care not to enter a range of addresses in use by any other DHCP services on your network or you will end up with conflicts. 
IP Address Range: The beginning and ending IP that will be manually handed out to client computers.
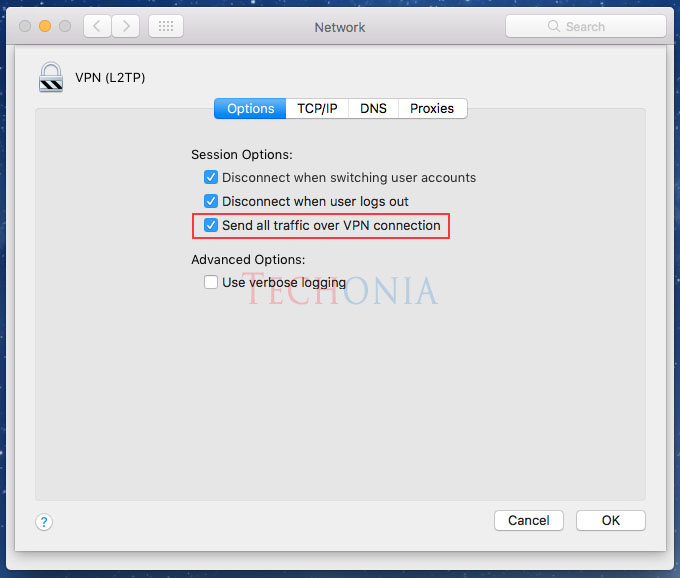 Allow 40-bit encryption keys: Allows clients to use lower levels of encryption. Shared Secret: The secret, or a second factor used with L2TP connection. Use custom accounts: Allows you to manually enter accounts to provide username and passwords for clients to connect to the. Use Directory Server: Allows you to use an LDAP or Active Directory connection to provide username and passwords to the service.
Allow 40-bit encryption keys: Allows clients to use lower levels of encryption. Shared Secret: The secret, or a second factor used with L2TP connection. Use custom accounts: Allows you to manually enter accounts to provide username and passwords for clients to connect to the. Use Directory Server: Allows you to use an LDAP or Active Directory connection to provide username and passwords to the service. #VPN REPLACEMENT FOR MAC SIERRA SERIAL#
Once installed, if you purchased the license separately, use the Enter Manually button to provide it.Īt the Registration screen, make sure the name, email, and serial are entered exactly as you see them in the email you received.Īt the EULA screen, click Accept assuming you accept the license agreement.Īt the main screen, you’ll have a few options, which we’ll unpack here:
#VPN REPLACEMENT FOR MAC SIERRA INSTALL#
You can install it manually as well, and if you do, you’ll need to pay separately through PayPal, which is what we’ll cover here. Another option would be to install iVPN from here, on the Mac App Store. That will require some work to get dependencies and some working with files and network settings. I decided not to cover it here because it uses Wine. One of the other tools Apple mentioned is SoftEther. OpenVPN has a lot of sweet options, which you can read about at. One would be to install openvpn: sudo port -v install openvpn2 There are a number of ways to get a VPN Server installed on macOS.
Enable VPN pass-through on the firewall of the server and client if needed. The following ports need to be opened per The Official iVPN Help Docs (these are likely already open if you’re using a macOS Server to provide VPN services): At this point, you can decide whether you want to dismantle the old server and setup a new one on the same IP address, or whether you’d rather just change your port forwards on your router/firewall.īefore we configure any VPN services, let’s talk about ports. Sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:2tp:L2TP:IPSecSharedSecretValueOnce we have all of this information, we can configure the new server using the same settings. Sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:2tp:DNS:OfferedServerAddresses:_array_indexįinally, if you’re using L2TP, let’s grab the shared secret: Sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers::DNS:OfferedServerAddresses:_array_index 
Sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers::IPv4:DestAddressRangesNow let’s grab the DNS servers handed out so those can be recreated: Sudo serveradmin settings vpn:Servers:2tp:enabledNext, we’ll get the the IP ranges used so we can mimic those (or change them) in the new service:






 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
